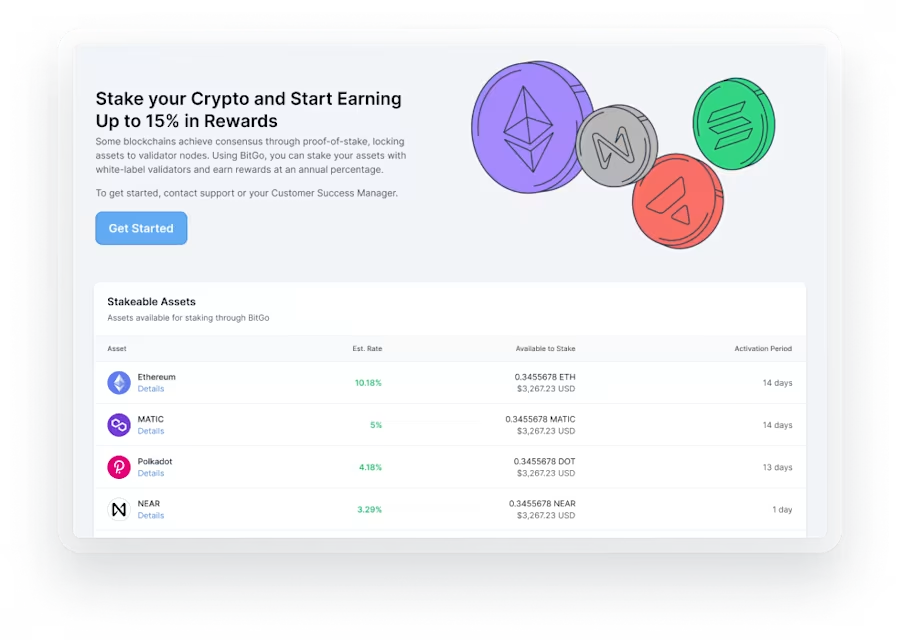
Staking vs. Delegated Staking: Understanding Your Options

Staking as a Service (SaaS) has surfaced as a convenient and accessible way for cryptocurrency investors to be involved in blockchain sites and earn rewards. This impressive method allows investors to delegate the specialized aspects of staking to a third-party service provider while experiencing the benefits of inactive revenue, network involvement, and potential money appreciation. Let's search into the benefits that staking offers to crypto investors.
Knowledge Staking as a Service
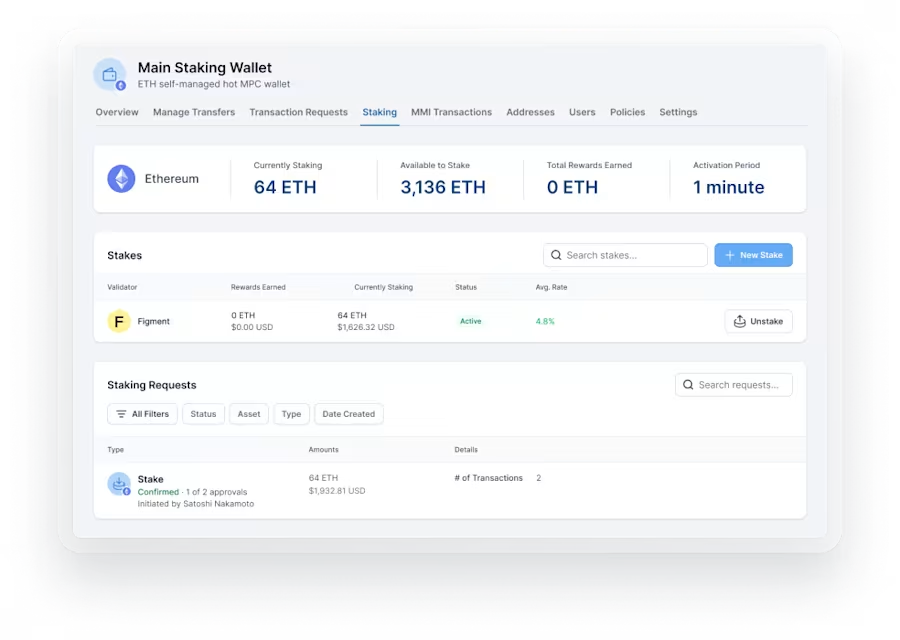
Staking as a Service involves outsourcing the staking method to a specific service service, frequently known as a staking provider or platform. Instead of handling the difficulties of working a staking node, maintaining wallet safety, and ensuring network uptime, investors may delegate these responsibilities to the service provider. In return, they get staking benefits and other benefits without the need for technical expertise or constant monitoring.
Advantages of Staking as a Service
1. Access to Inactive Income:
One of many principal advantages of Staking as a Service is the opportunity to generate passive income from staking rewards. By delegating their tokens to a staking service, investors can be involved in the staking process without actively controlling a staking node or maintaining wallet security. That passive income stream can supplement conventional investment techniques and offer a constant return on investment.
2. Elimination of Complex Complexity:
Working a staking node requires complex familiarity with blockchain protocols, budget administration, and network security. Staking as a Service simplifies this method by outsourcing all complex features to experienced service providers. Investors benefit from the provider's experience in maintaining nodes, ensuring uptime, and handling project updates, letting them focus on investment technique as opposed to complex operations.
3. Diversification and Chance Administration:
Staking as a Service helps investors to diversify their cryptocurrency holdings across numerous staking tools and protocols. Rather than focusing resources on a single blockchain system, investors may spend their tokens to various staking services, distributing risk and possibly increasing rewards. That diversification strategy increases profile resilience and mitigates the influence of market fluctuations on attached assets.
4. Variable Staking Possibilities:
Staking as a Service presents freedom with regards to staking options and token liquidity. Investors can decide from various staking intervals, incentive structures, and withdrawal choices depending on the expense goals and chance tolerance. Some companies present quick liquidity choices, letting investors to withdraw secured tokens or benefits without extended lock-up periods, increasing liquidity management.
5. Increased Protection and Consistency:
Dependable Staking as a Service vendors prioritize security measures to safeguard investors' resources and assure the reliability of staking operations. These providers employ effective security protocols, such as cool storage wallets, multi-factor authentication, and standard protection audits, to safeguard secured tokens against unauthorized entry and possible cyber threats. Investors take advantage of enhanced security without compromising on staking rewards.
6. Involvement in Governance:
Many Staking as a Service platforms present investors the ability to be involved in blockchain system governance. Token cases can election on method improvements, governance proposals, and environment developments, influencing the long run direction of the network. That active participation empowers investors to subscribe to decentralized governance and arrange their passions with the long-term accomplishment of the blockchain platform.
Concerns for Investors
1. Service Service Name and Track Report:
Before choosing a Staking as a Service service, investors should perform complete due homework on the provider's name, background, and security practices. Evaluations, testimonies, and neighborhood feedback provides valuable insights into the consistency and trustworthiness of the service provider.
2. Fee Structures and Visibility:
It's essential to know the cost structures associated with Staking as a Service , including management charges, efficiency costs, and withdrawal fees. Translucent fee disclosure assures investors can precisely gauge the cost-effectiveness of the service and produce knowledgeable decisions about staking participation.
3. Regulatory Submission and Legal Considerations:
Cryptocurrency regulations vary across jurisdictions, and investors should make certain that Staking as a Service conforms with appropriate regulatory requirements. Knowledge appropriate concerns, duty implications, and compliance obligations can mitigate regulatory risks and ensure appropriate compliance when participating in staking activities.
Conclusion
Staking as a Service presents engaging advantages for cryptocurrency investors seeking to earn inactive revenue, be involved in blockchain systems, and diversify their expense portfolios. By outsourcing the complex difficulties of staking to experienced service providers, investors can enjoy enhanced security, freedom, and involvement in blockchain governance. Nevertheless, it's essential for investors to perform thorough study, examine risk facets, and select reliable service suppliers to maximise the benefits of Staking as a Service effectively.
